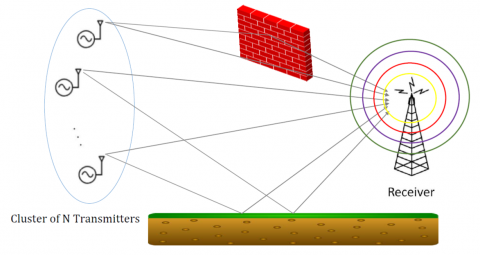
Distributed beamforming is a form of cooperative communication in which two or more sources simultaneously transmit a common message and control the phase and frequency of their transmissions so that the signals constructively combine at an intended destination. We consider distributed transmit beamforming from a cluster of cooperating nodes towards a distant destination, over a wideband dispersive channel as shown in Figure-1. Explicit aggregate feedback is used where the destination broadcasting its feedback to all nodes in the transmit cluster. Explicit feedback allows for frequency division duplex (FDD) operation, since there is no reliance on channel reciprocity.
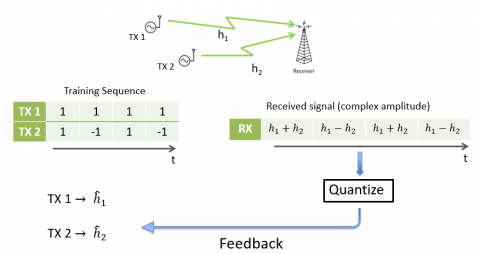
To provide beamforming in a narrowband setting, transmitters use a training-based approach to estimate their channel based on heavily quantized aggregate feedback from receiver. This framework is resilient to noise and an example with 2 transmitters are shown in Figure - 2.
Narrowband scheme is extended to wideband by using OFDM. Training only on subset of subcarriers is sufficient to achieve beamforming by using interpolation across subcarriers using sparse time domain modeling of channel estimates.